As part of your organisations cyber governance and risk management program, we recommend adopting a set of industry-standard cyber security controls that provide strong baseline security. We assist clients to understand cyber governance, implement a programme of work, undertake an assessment of current state, and formulate a suitable roadmap for improvement to reduce your cyber risk.
When it comes to securing your organisation, the CIS Critical Security Controls provide a prioritised, prescriptive set of best practices used globally to improve cyber resilience. At Incident Response Solutions, we help you turn these recommendations into measurable outcomes, ensuring your defences are aligned with a standard of excellence. By assessing your current state against the CIS framework, wealso provide the confidence you require to Prepare, Respond, and Recover from incidents effectively.
How We Can Help
Our CIS engagements are designed to be a practical roadmap, not just a checklist. We help you move from theory to execution with expert-led guidance tailored to your specific environment.
- Benchmark Your Controls: Evaluate your current security measures against the latest CIS framework to see where you stand.
- Identify and Prioritise Gaps: Surface the vulnerabilities that expose your organisation to the greatest risk.
- Actionable Remediation: We provide a clear path forward with practical steps to strengthen your defence-in-depth.
Centre for Internet Security (CIS) Controls
The CIS Controls are a relatively small number of prioritised, well-vetted, and supported security actions that organisations can take to assess and improve their current security state. The controls are designed using knowledge of actual attacks to help an organisation prioritise their investment in controls that will provide the greatest risk reduction and protection against the most dangerous threat actors, and that can be feasibly implemented.
To prioritise the subset of controls to be implemented by a business, CIS uses “Implementation Groups (IGs)” which are self-assessed categories based on relevant cybersecurity attributes. Each IG is linked to a subset of the CIS Controls that the broader security community has assessed to be reasonable for an organisation with a similar risk profile and resources to strive to implement. At a high level, the three IG group definitions are:
- Implementation Group 1 – A small or medium-sized organisation with limited resources and cybersecurity expertise available to implement Sub-Controls.
- Implementation Group 2 – An organisation with moderate resources and cybersecurity expertise to implement Sub-Controls.
- Implementation Group 3 – A mature organisation with significant resources and cybersecurity experience to allocate to Sub-Controls.
There are 18 CIS controls in total and 153 safeguards (sub controls) that can guide you in creating a layered or defence-in-depth cybersecurity strategy. This latest version focuses more heavily on cloud-based computing (full and hybrid environments), virtualisation, outsourcing, work-from-home and mobility. It also recognises changing attacker tactics, which we summarise below and in the corresponding links for each control.
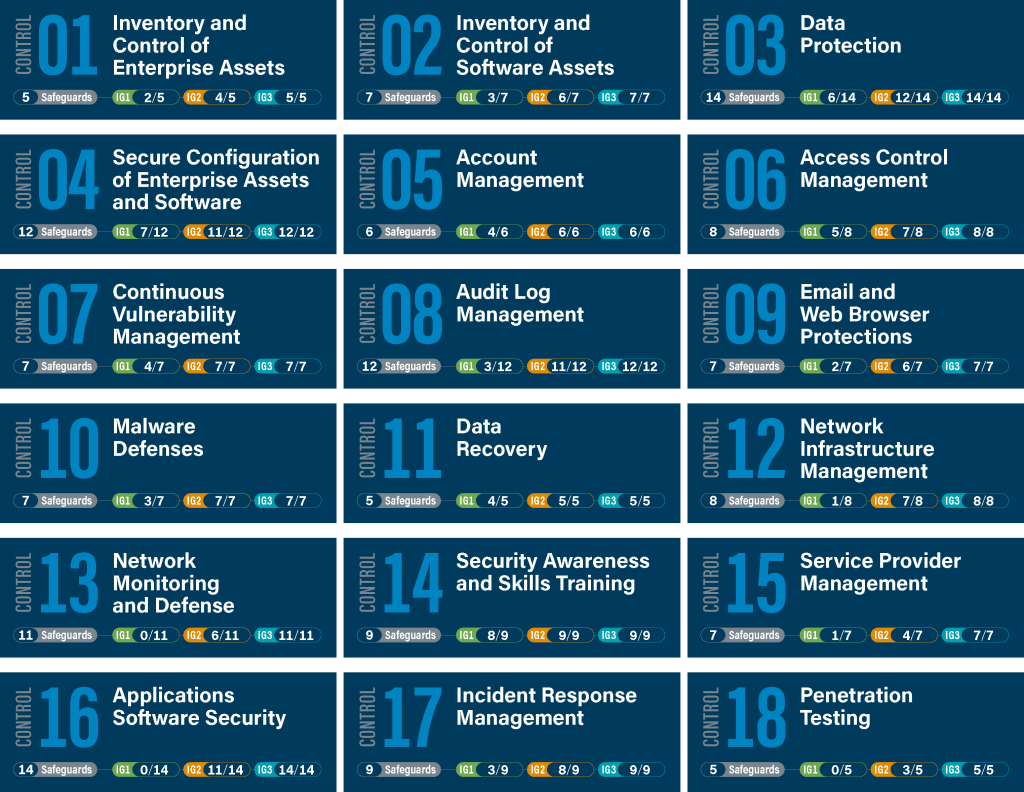
CIS Control 1: Inventory and Control of Enterprise Assets
Actively manage all enterprise assets connected to the infrastructure physically, virtually, remotely, and those within cloud environments, to accurately know the totality of assets that need to be monitored and protected within the enterprise. This will also support identifying unauthorized and unmanaged assets to remove or remediate.
CIS Control 2: Inventory and Control of Software Assets
Actively manage (inventory, track, and correct) all software (operating systems and applications) on the network so that only authorized software is installed and can execute, and that unauthorized and unmanaged software is found and prevented from installation or execution.
CIS Control 3: Data Protection
Develop processes and technical controls to identify, classify, securely handle, retain, and dispose of data.
CIS Control 4: Secure Configuration of Enterprise Assets and Software
Establish and maintain the secure configuration of enterprise assets and software
CIS Control 5: Account Management
Use processes and tools to assign and manage authorization to credentials for user accounts, including administrator accounts, as well as service accounts, to enterprise assets and software.
CIS Control 6: Access Control Management
Use processes and tools to create, assign, manage, and revoke access credentials and privileges for user, administrator, and service accounts for enterprise assets and software.
CIS Control 7: Continuous Vulnerability Management
Continuously acquire, assess, and take action on new information in order to identify vulnerabilities, remediate, and minimise the window of opportunity for attackers.
CIS Control 8: Audit Log Management
Collect, alert, review, and retain audit logs of events that could help detect, understand, or recover from an attack.
CIS Control 9: Email and Web Browser Protections
Improve protections and detections of threats from email and web vectors, as these are opportunities for attackers to manipulate human behavior through direct engagement.
CIS Control 10: Malware Defenses
Prevent or control the installation, spread, and execution of malicious applications, code, or scripts on enterprise assets.
Establish and maintain data recovery practices sufficient to restore in-scope enterprise assets to a pre-incident and trusted state.
CIS Control 12: Network Infrastructure Management
Establish, implement, and actively manage (track, report, correct) network devices, in order to prevent attackers from exploiting vulnerable network services and access points.
CIS Control 13: Network Monitoring and Defense
Operate processes and tooling to establish and maintain comprehensive network monitoring and defense against security threats across the enterprise’s network infrastructure and user base.
CIS Control 14: Security Awareness and Skills Training
Establish and maintain a security awareness program to influence behavior among the workforce to be security conscious and properly skilled to reduce cybersecurity risks to the enterprise.
CIS Control 15: Service Provider Management
Develop a process to evaluate service providers who hold sensitive data, or are responsible for an enterprise’s critical IT platforms or processes, to ensure these providers are protecting those platforms and data appropriately.
CIS Control 16: Application Software Security
Manage the security life cycle of in-house developed, hosted, or acquired software to prevent, detect, and remediate security weaknesses before they can impact the enterprise.
CIS Control 17: Incident Response Management
Establish a program to develop and maintain an incident response capability (e.g., policies, plans, procedures, defined roles, training, and communications) to prepare, detect, and quickly respond to an attack.
CIS Control 18: Penetration Testing
Test the effectiveness and resiliency of enterprise assets through identifying and exploiting weaknesses in controls (people, processes, and technology), and simulating the objectives and actions of an attacker.
Contact us to arrange a consultation.
