Control Summary
Use processes and tools to create, assign, manage, and revoke access credentials and privileges for user, administrator, and service accounts for enterprise assets and software.
Why is it needed?
While CIS Control 5 primarily focuses on account management, CIS Control 6 shifts its attention to overseeing the access granted to these accounts. It aims to ensure that users are only provided access to data or enterprise assets that align with their specific roles and responsibilities. Furthermore, it emphasises the implementation of robust authentication measures, particularly for critical or sensitive enterprise data and functions. It is imperative that accounts are configured with the least privilege required for their respective roles, and establishing consistent access rights for each role while assigning them to users is considered a best practice. Additionally, the development of a comprehensive program for both provisioning and de-provisioning access holds significant importance, with centralisation being the preferred approach.
Certain user activities carry elevated risk levels for an enterprise. These activities may involve access from untrusted networks or the execution of administrative functions, granting the ability to add, modify, or remove other accounts, as well as make configuration changes to operating systems or applications that could compromise security. This underscores the critical need for the adoption of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Privileged Access Management (PAM) tools to bolster security measures.
Implementing Control
Whilst CIS control 5 manages account creation and deletion; this control is about effectively determining what access all accounts have and ensuring users only have access to the data or enterprise assets appropriate for their role. Strong authentication must also be enabled for critical or sensitive data or functions.
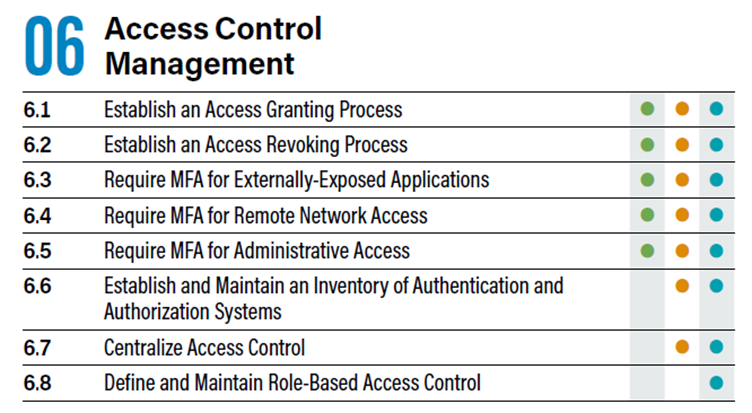
Implementation Group 1 requires the following five safeguards:
6.1 Establish an Access Granting Process
Establish and adhere to a procedure, preferably automated, for provisioning access to enterprise assets when onboarding new employees, granting rights, or altering user roles.
6.2 Establish an Access Revoking Process
Set up and adhere to a procedure, preferably automated, for revoking access to enterprise assets by promptly disabling accounts upon employee terminations, rights revocation, or changes in user roles. The decision to disable rather than delete accounts may be essential to maintain comprehensive audit trails.
6.3 Require MFA for Externally-Exposed Applications
MFA should be in place for externally exposed applications.
6.4 Require MFA for Remote Network Access
MFA should also be in place for remote network access.
6.5 Require MFA for Administrative Access
MFA should be in place for all privileged or administrator accounts as a minimum. In addition, specialised Privileged Access Management (PAM) tools, that require a provided one-time password to be checked out for each use, should be considered.
Additional safeguards at level 2 or 3:
6.6 Establish and Maintain an Inventory of Authentication and Authorisation Systems
6.7 Centralize Access Control
6.8 Define and Maintain Role-Based Access Control
