Control Summary
Establish a program to develop and maintain an incident response capability to prepare, detect, and quickly respond to an attack.
Why is it needed?
A robust cyber security strategy encompasses protective measures, threat detection capabilities, rapid incident response protocols, and resilient recovery procedures. Oftentimes, the latter two components tend to be neglected. In some cases, the response to a compromised system boils down to merely restoring it to its original state and moving forward. The core objective of incident response is to swiftly identify threats within the organisation, take decisive action to contain them before they propagate, and then implement remediation steps to prevent further harm. Failing to grasp the complete scope of an incident, its origins, and the preventive measures needed would result in security practitioners being trapped in a perpetual ‘whack-a-mole’ cycle.
We must acknowledge that even the most robust protective measures cannot guarantee 100% effectiveness. When a security incident inevitably occurs, an organisation without a well-documented plan will struggle to execute appropriate investigative procedures, establish clear reporting channels, collect critical data, assign management responsibilities, adhere to legal protocols, and devise a coherent communications strategy. These elements are vital for an organisation to successfully comprehend, manage, and recover from security incidents, even when staffed with competent cybersecurity professionals.
Implementing Control
This control includes safeguards that constitute minimum basic security hygiene for all businesses. Even small organisations with limited resources to conduct incident response activities should have an incident response plan. The plan at a minimum should identify the source of protections and detections (e.g.: where an alert or notification of a potential cyber incident may come from), a list of who to call upon for assistance, and communication plans and mechanisms to inform required parties such as leadership, employees, regulators, partners, and customers.
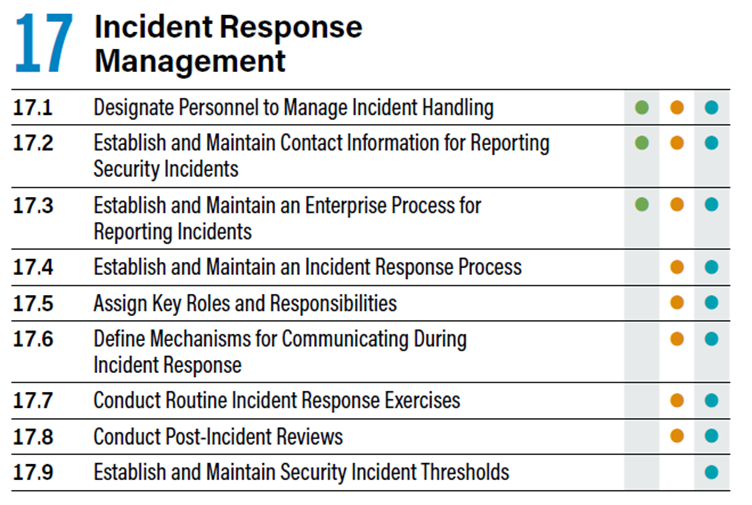
Implementation Group 1 requires the following three safeguards:
17.1 Designate Personnel to Manage Incident Handling
Appoint a primary individual, along with at least one backup, to oversee the enterprise’s incident handling process. These management personnel bear the responsibility of coordinating and documenting incident response and recovery efforts. They may include internal employees, third-party vendors, or a combination of both in a hybrid approach.
17.2 Establish and Maintain Contact Information for Reporting Security Incidents
Set up and uphold a repository of contact details for individuals or entities that must be notified in the event of security incidents. These contacts may comprise internal personnel, third-party vendors, law enforcement agencies, cyber insurance providers, pertinent government bodies, Information Sharing and Analysis Center (ISAC) collaborators, or other relevant stakeholders. Conduct annual verifications of these contacts to guarantee that the information remains current and accurate.
17.3 Establish and Maintain an Enterprise Process for Reporting Incidents
Create and sustain a systematic procedure within the enterprise for the workforce to report security incidents. This procedure should outline the reporting timeline, specify the individuals to whom incidents should be reported, detail the reporting mechanisms, and define the essential information that must be included in the report. Ensure that this process is readily accessible to all members of the workforce. Periodically review it on an annual basis or whenever substantial changes within the enterprise could affect this security measure.
Additional safeguards at level 2 or 3:
17.4 Establish and Maintain an Incident Response Process
17.5 Assign Key Roles and Responsibilities
17.6 Define Mechanisms for Communicating During Incident Response
17.7 Conduct Routine Incident Response Exercises
17.8 Conduct Post-Incident Reviews
17.9 Establish and Maintain Security Incident Thresholds
